Silicon IP Cores
SPI2AHB
SPI to AHB-Lite Bridge
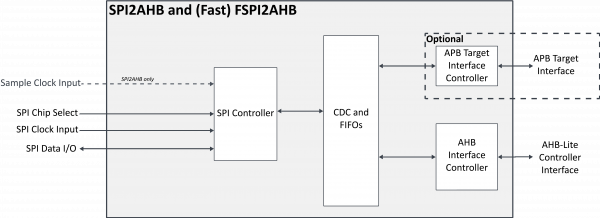
The SPI2AHB core implements an SPI slave to AHB-Lite master bridge. It allows an external SPI master to perform read or write access to any memory-mapped device on the internal AHB bus.
The core implements a simple over-SPI protocol to convert SPI transactions into AHB Read or Write instructions. This over-SPI protocol supports variable-length data accesses, which are translated to AHB-Lite accesses on the AHB-Lite master port. The bridge also monitors the AHB-Lite bus and reports erroneous transfers to the system. Errors captured by the core include Error Responses on the AHB bus, and errors due to slow responses for the accessed AHB-Lite slave.
The core supports single, dual, quad, and octal SPI data lines. The lower-level SPI transmission format is compliant to the SPI de facto standard but fixed to minimize area and power. The core drives the outbound serial data on the rising edge of the serial clock, and samples inbound serial data on the negative edge of the serial clock (CPHA=1) while the resting state of the serial clock is low (CPOL=0).
The SPI2AHB is designed with industry best practices, and its reliability and low risk have been proven through both rigorous verification and customer production. It is available in Verilog RTL source or as a targeted FPGA netlist, and its deliverables in-clude sample synthesis and simulation scripts and comprehensive user documentation.
The SPI2AHB core is available in two versions: the standard (spi2ahb) and the fast (fspi2ahb). The differences between the two versions are:
- The fast version supports both a 32-bit and 64-bit AHB-lite bus, while the standard version supports only 32-bit
- The fast version is partially clocked by the serial SPI clock and an inverted version of it. The standard version treats the serial clock as a data line that is sampled using an externally provided clock, which needs to be at least 8 times faster than the serial SPI clock. Constraining the fast version is therefore a bit more demanding than constraining the standard version.
- The fast version supports data-strobe (DQS) signals, while the standard version does not
- The fast version supports byte-level access while the standard supports only word-level access
The SPI2AHB enables an external device to have full access to the internal AHB-Lite bus over an SPI connection. It can be used for firmware uploads, design initialization, and run-time monitor, control, and debug in a wide variety of designs including typical microcontrollers, sensors, MEMs, and analogue front ends.
The core as delivered is warranted against defects for ninety days from purchase. Thirty days of phone and email technical support are included, starting with the first interaction. Additional maintenance and support options are available.
Engineered by Beyond Semiconductor.
Features List
Enables an external device to have full access to the internal AHB-Lite bus over an SPI connection.
Typical Use-Cases
- Firmware upload over SPI
- Monitor and Control over SPI
- e.g. Analog Front End or MEMs initialization and calibration over SPI
- Debug Over SPI
Interfaces
- SPI-Slave Interface
- Single, Dual, Quad, and Octal serial data lines
- Fixed transmission format (CPOL=0, CPHA=1) for lower area and power
- 32-bit or 64-bit AHB-Lite Master Interface
- Optional 32-bit APB slave interface for CSR access
Easy Integration
- Independent serial and system (AHB bus) clocks
- CDC-Clean design
- Bus Error Reporting
- Core monitors the AHB Lite bus and reports erroneous transfers and error type to registers accessible via SPI and via an APB interface.
Deliverables
- Verilog RTL source code or targeted FPGA netlist
- User Documentation
- Sample synthesis and simulation scripts